
TBEP
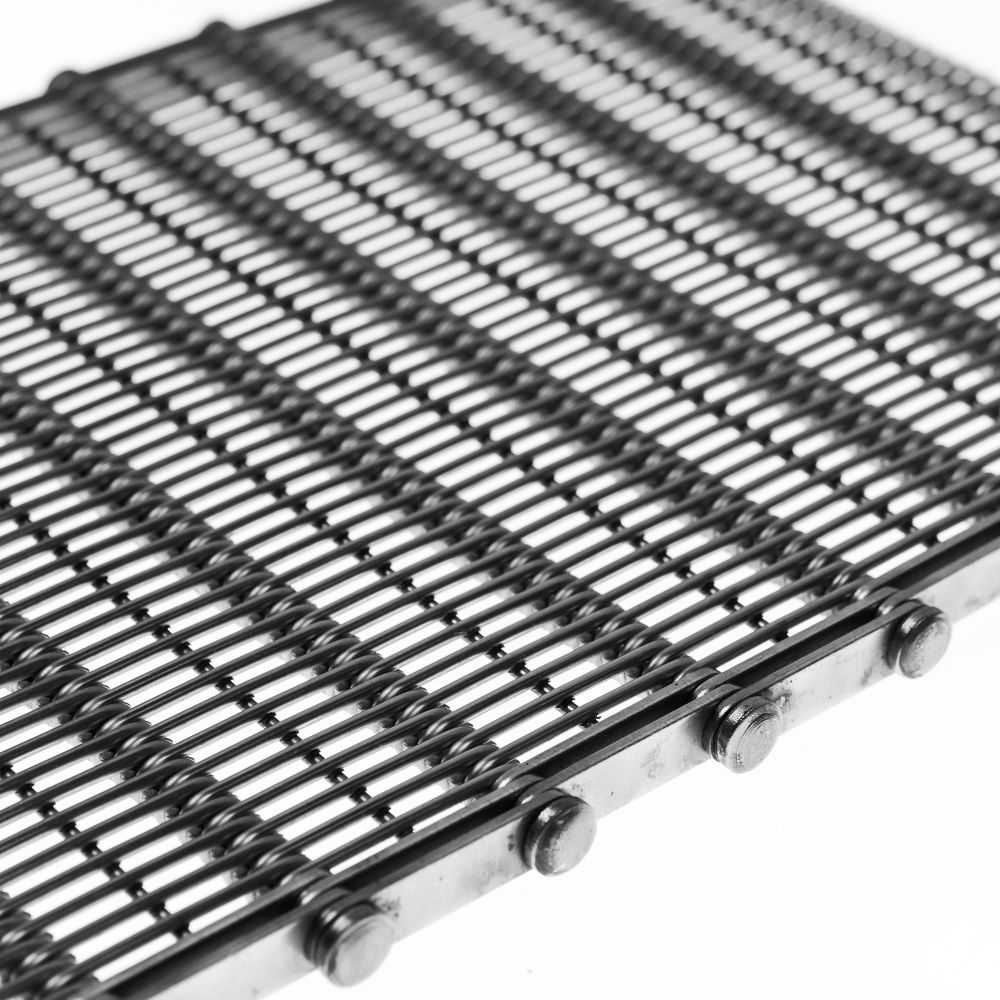
Wire is welded between the eye-links to make it more stable and durable. Thanks to this welding, the distance between the eye-links can be increased. It is a lighter model. But it is not suitable for heavy loads and harsh conditions. The number of rods to be tack welded onto eye-links can be one or two
TBEP - Technical Drawing (Eye- Link Conveyor Belt)
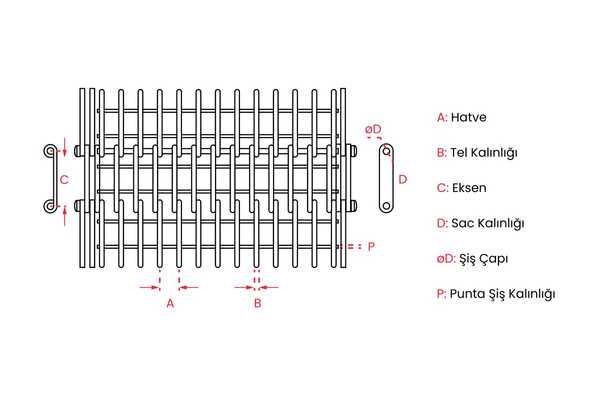
TBEP - Dimensions: (Eye- Link Conveyor Belt)
| B: Wire Diameter | C: Rod pitch | S: Chain Rod Diameter | D: Rod Diameter |
| 1,5 2,0 2,5 3,0 3,5 | 30 50 50,8 75 | 3 4 5 | 4 5 7 8 |
Types: Eye- Link Conveyor Belt
TBE
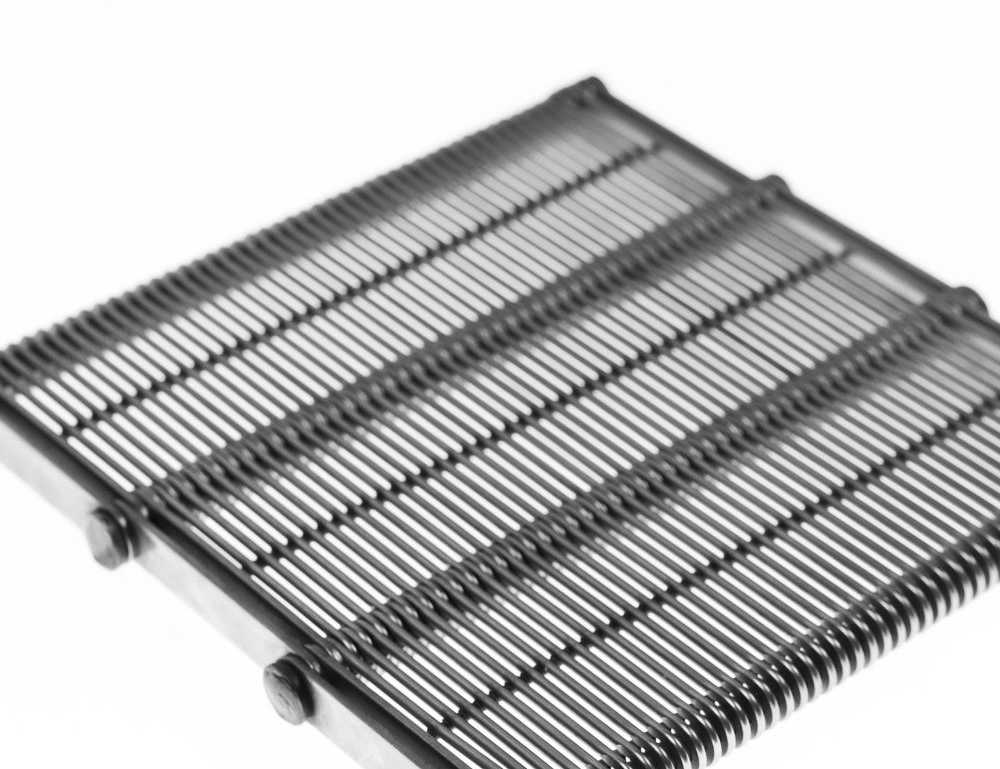

This conveyor belt model is formed by placing wire loops (eye-links) without gaps between them. The space between the eye-links is the same as the thickness of the wire. It can be preferred in cases where the amount of space in the conveyor belt is not needed (air & luquid flow rate) and the material carried is poured heavy and/or from a certain height.
TBF
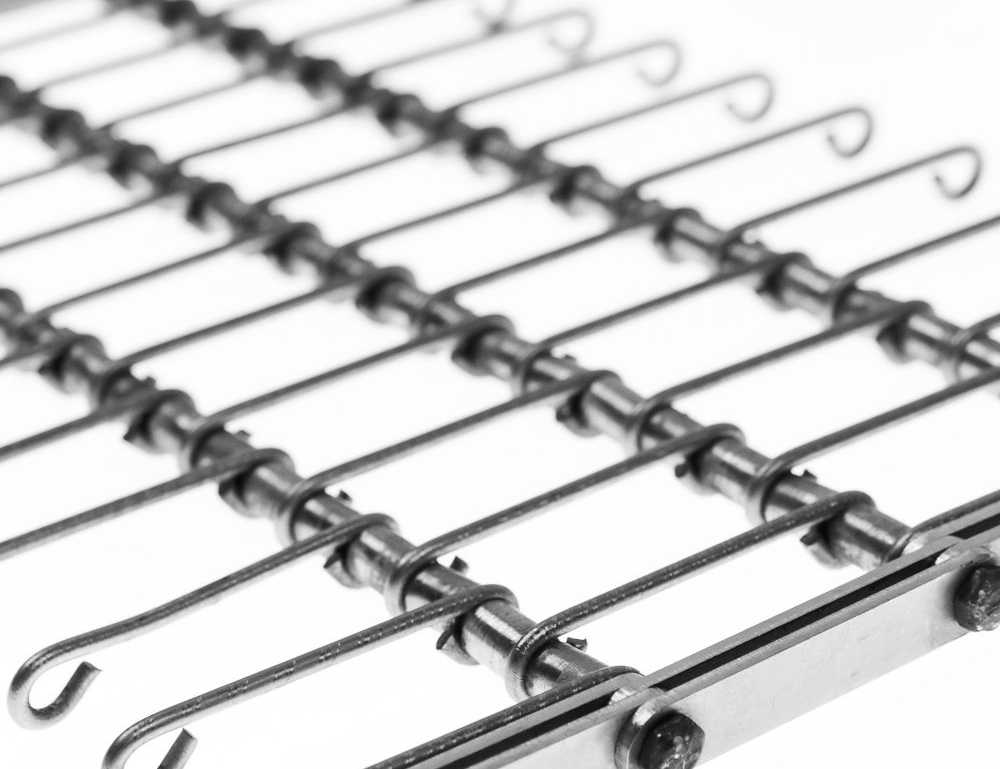

This conveyor belt model is produced by placing a bush or spring between the eye-links. With these bush and spring placement, the desired amount of space and permeability are provided. If the bushing is placed between the eye-links, the conveyor belt becomes heavier, stable and resistant to vertical high forces. If the spring is placed, the conveyor belt becomes more resistant to horizontal forces and shocks. Also it is a lighter conveyor belt model than others.
